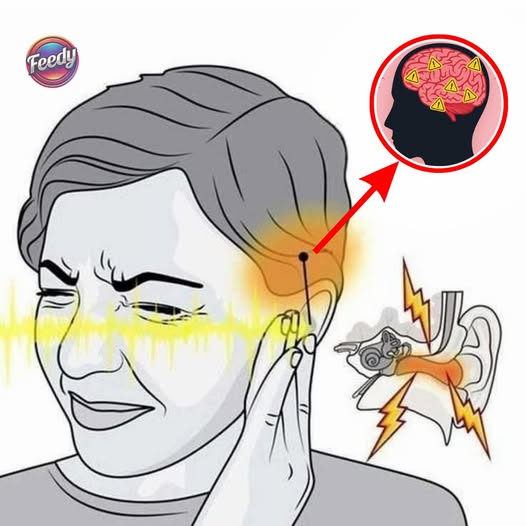
Tinnitus, the persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears, can be frustrating and disruptive. While there is no universal cure, several practical strategies can help you manage the symptoms and regain control over your daily life.
1. Protect Your Hearing 🛑🔊
- Avoid loud noises that can worsen tinnitus, such as concerts, fireworks, or power tools.
- Wear ear protection (earplugs or noise-canceling headphones) in noisy environments.
- Lower the volume on your devices, especially when using headphones.
2. Keep Your Ears Clean 👂✨
- Excess earwax buildup can contribute to tinnitus. Use gentle ear-cleaning methods, like warm water or over-the-counter drops.
- Avoid cotton swabs, as they can push wax deeper into the ear canal.
- Visit a doctor if you suspect a blockage or need professional ear cleaning.
3. Reduce Stress and Anxiety 🧘♀️💆
Stress can make tinnitus worse. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as:
✔ Deep breathing exercises
✔ Meditation or mindfulness
✔ Yoga and gentle stretching
✔ Listening to calming music or nature sounds
4. Try Sound Therapy 🎶🌿
Soothing background sounds can help mask tinnitus, making it less noticeable. Try using:
- White noise machines or apps
- Soft music or nature sounds (ocean waves, rainfall)
- A fan or air purifier for a subtle background hum
5. Consider Hearing Aids 🎧👂
If you have hearing loss, tinnitus may seem more pronounced due to the lack of external sounds. Hearing aids can:
✔ Enhance ambient noises to make tinnitus less noticeable
✔ Improve overall hearing clarity
✔ Reduce strain on your ears
6. Watch Your Diet and Lifestyle 🥦☕❌
Certain foods and habits can trigger or worsen tinnitus. Try to:
- Limit caffeine and alcohol, as they can overstimulate the nervous system.
- Reduce salt intake, as high sodium levels can affect blood circulation in the ears.
- Quit smoking, since nicotine can restrict blood flow and worsen symptoms.
- Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
7. Consider Medical Consultation 🩺👨⚕️
Although there’s no specific cure for tinnitus, some treatments can help:
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to reframe how you react to tinnitus.
- Medications (like antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs) in severe cases.
- Zinc or magnesium supplements, which may support ear health (consult your doctor first).
When to See a Doctor ❗🩺
Seek medical attention if your tinnitus:
✔ Lasts for more than a week without improvement
✔ Interferes with your sleep, work, or daily activities
✔ Is accompanied by dizziness, hearing loss, or ear pain
An ENT specialist (ear, nose, and throat doctor) or audiologist can evaluate the condition and recommend treatments tailored to your needs.
Final Thoughts 💡
Tinnitus can be manageable with the right strategies. By protecting your hearing, managing stress, and making lifestyle adjustments, you can reduce its impact and improve your overall well-being.